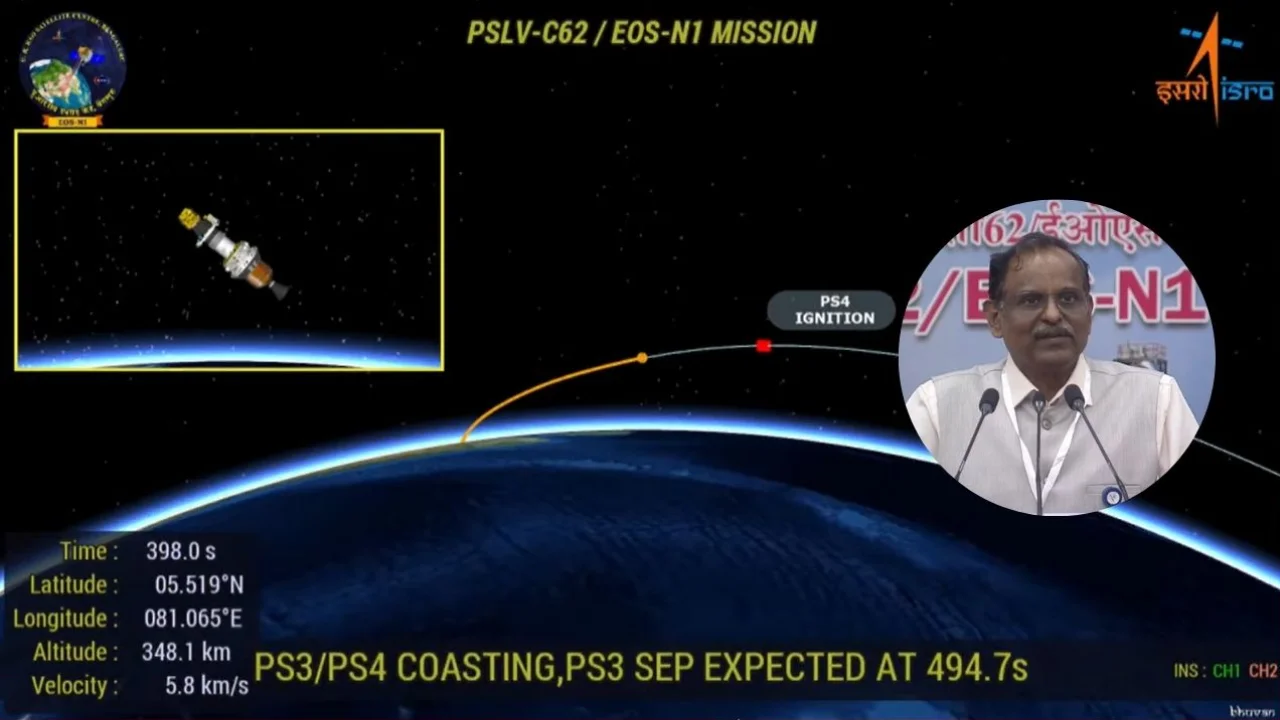
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) experienced a rare setback on Monday as the PSLV-C62 mission failed to deploy its primary payload into the intended orbit. Despite a perfect liftoff from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota, a technical glitch during the third stage of the flight caused the rocket to deviate from its path, leaving the satellites stranded.
High-Stakes Mission Ends in Technical Glitch
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), often called ISRO’s “reliable workhorse,” took off from the First Launch Pad with 15 satellites on board. While the initial phases of the flight proceeded as planned, an anomaly was detected at the end of the PS3 (third stage).
This disruption altered the flight trajectory, preventing the satellites from reaching the precise altitude and inclination required. ISRO confirmed the news via social media, stating that a detailed analysis has been initiated to understand the root cause of the deviation.
The Loss of ‘Anvesha’: India’s Advanced Eyes in the Sky
The primary casualty of this mission is Anvesha, a cutting-edge satellite developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Target Orbit: It was scheduled to be placed in a Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit (SSO) at an altitude of 600 km.
- Strategic Importance: Anvesha is a high-tech “spy satellite” designed for precision surveillance and mapping.
- Unique Capability: Equipped with Hyperspectral Remote Sensing (HRS) technology, it can detect hundreds of subtle light spectrums. This allows it to “see” through camouflage, identifying enemies hidden in dense forests, bunkers, or bushes by analyzing the unique light signatures of different materials.
A Major Commercial Blow for NSIL
The PSLV-C62 was the 64th flight of the PSLV and the 9th dedicated commercial mission managed by NewSpace India Limited (NSIL). The mission was carrying a total of 15 satellites, representing a mix of domestic innovation and international partnerships.
Satellite Mission Breakdown:
| Category | Number of Satellites | Origin Countries |
| Indian Satellites | 07 | India (including Dhruva Space) |
| Foreign Satellites | 08 | France, Nepal, Brazil, UK |
| Total | 15 |
This mission was particularly significant for India’s private space sector. Hyderabad-based Dhruva Space had seven satellites on board, marking one of the largest participations by a private Indian firm in a single PSLV mission.
ISRO Chief’s Statement: “Data Under Analysis”
Addressing the mission outcome, the ISRO Chairman stated that the issue originated in the third stage, leading to a change in direction. “The data is currently being analyzed. We will provide further updates as soon as the investigation yields specific results,” he added.
While the PSLV has an incredible track record—having successfully launched iconic missions like Chandrayaan-1, Mangalyaan, and Aditya-L1—this incident serves as a reminder of the immense complexities and risks involved in space exploration.
What is Hyperspectral Technology?
The failure is a significant loss for the scientific community because of the Anvesha’s HRS technology. Unlike standard cameras that capture basic colors, Anvesha acts like a molecular scanner. It can distinguish between different types of soil, vegetation, and man-made structures based on their specific light reflection, providing Indian defense forces with unparalleled intelligence.